
Data labeling is the process of adding meaningful tags, annotations, or categories to raw data like images, text, audio, or video. Think of it as putting the right labels on items in a supermarket - it helps machines understand what they're looking at and learn from the information.
Consider teaching a child to recognize animals. You show them pictures and say "this is a cat" or "this is a dog." Data labeling works similarly - we're teaching machines to recognize patterns by providing them with labeled examples they can learn from.
In this blog, we will explore this concept further and explain the different types of data labeling, its importance, its applications, and the data labeling process.
In artificial intelligence and machine learning, labeled data serves as the fundamental cornerstone for training robust and accurate models. Just as a student needs well-explained examples to master mathematics, AI applications require meticulously labeled data to understand patterns, make predictions, and perform complex tasks with precision.
The quality of data labeling has a direct and profound impact on model performance. When data is labeled incorrectly or inconsistently, it creates confusion in the learning process, similar to how conflicting or incorrect information would confuse a student. This confusion can lead to model bias, poor generalization, and unreliable predictions in real-world applications.

Consider an AI system being trained to detect medical conditions in X-rays. If the training data contains mislabeled examples or inconsistent annotations of medical conditions, the model might learn incorrect patterns. This could result in missed diagnoses or false positives when deployed in clinical settings, potentially affecting patient care outcomes.
Companies invest substantial resources in ensuring their data labeling processes are precise and consistent because they understand this critical relationship between data quality and model performance. This investment includes hiring domain experts, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and utilizing specialized tools and platforms for accurate labeling.
The impact of high-quality labeled data extends beyond initial model training:
For instance, a model trained on well-labeled general image data can be fine-tuned more effectively for specific tasks like satellite imagery analysis or medical imaging.
The relationship between data labeling quality and model performance emphasizes the need for systematic approaches to data annotation. This includes,
Investing in quality data labeling is crucial for ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of AI applications in real-world scenarios.
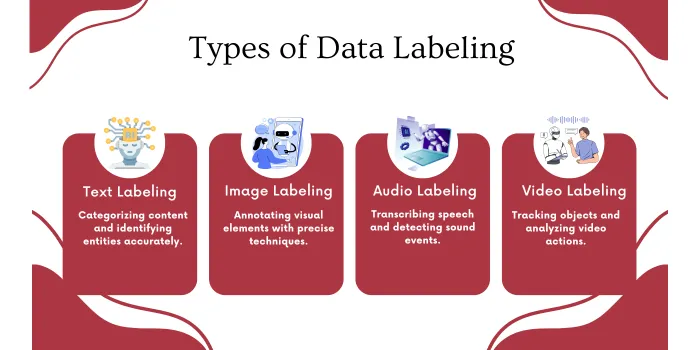
Just as humans learn to understand words, pictures, sounds, and videos, machines require different types of labeled data to interpret various forms of information effectively.
Let's explore how we label different types of data.
Text labeling focuses on categorizing written content, identifying entities, and marking sentence structures. This includes tasks like sentiment analysis, topic classification, and named entity recognition. Accuracy in text labeling requires understanding context and language nuances.
Modern text labeling often involves understanding multiple languages and dialects. Labelers must consider cultural context, idiomatic expressions, and regional variations to create truly useful training data for natural language processing systems.
Image labeling requires precise annotation of visual elements within pictures. This includes bounding boxes around objects, segmentation masks for detailed object boundaries, and keypoint marking for pose estimation. Each technique serves different machine learning objectives.
Advanced image labeling may involve 3D point cloud annotation, depth estimation, and scene understanding. These complex tasks require specialized tools and expertise to ensure an accurate representation of spatial relationships and object interactions.
Audio labeling encompasses speech transcription, speaker identification, and sound event detection. Labelers must mark timestamps, identify different speakers, and categorize various audio events with high precision.
Quality audio labeling requires understanding acoustic properties, speech patterns, and background noise characteristics. This helps create robust training data for speech recognition and audio processing systems.
Video labeling combines elements of image and audio labeling while adding temporal dimensions. This includes object tracking, action recognition, and scene segmentation across multiple frames. The complexity increases with video length and scene dynamics.
Advanced video labeling may involve 3D motion tracking, behavioral analysis, and event detection. These tasks require sophisticated tools and experienced labelers who understand both spatial and temporal relationships.

Data labeling follows a structured path from raw information to a finished product that machines can learn from effectively. Like any well-designed production process, it involves careful planning, systematic execution, and thorough quality checks at every stage.
Let’s explore each stage in detail below.
The journey begins with gathering diverse, representative data from various sources. This includes considerations for data quality, variety, and legal compliance. Proper sampling strategies ensure balanced and unbiased datasets.
Before labeling begins, data must be cleaned, normalized, and organized. This involves removing duplicates, handling missing values, and standardizing formats. Quality preprocessing saves time and improves labeling accuracy.
Establishing efficient workflows involves creating detailed guidelines, training labelers, and implementing quality control measures. Clear communication channels and feedback loops help maintain consistency across teams.
Multiple validation layers ensure labeling accuracy. This includes peer reviews, expert verification, and statistical quality metrics. Regular audits help identify and correct systematic errors before they impact model training.
Modern data labeling relies on specialized software and platforms that help teams work efficiently and maintain high quality standards. These tools range from basic annotation software to sophisticated platforms powered by artificial intelligence, all designed to streamline the labeling process and ensure accuracy.
Modern platforms offer features like automated pre-labeling, quality control workflows, and collaboration tools. These systems help scale labeling operations while maintaining quality standards.
Popular data labeling tools include Labelbox, which streamlines workflows and enhances model accuracy, and SuperAnnotate, known for its robust annotation features and AI-driven automation.
Data labeling powers AI solutions across numerous business sectors, from healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing. Each industry uses labeled data differently to solve unique challenges, improve operations, and create better products and services for their customers.
Medical image labeling requires extreme precision and expert knowledge. Radiologists and specialists contribute to creating high-quality training data for diagnostic AI applications.
Healthcare applications extend to patient record analysis, medical terminology extraction, and symptom classification. Each application requires specific expertise and careful attention to medical privacy regulations.
Financial data labeling application includes transaction classification, fraud detection patterns, and market trend analysis. Accuracy is crucial given the high stakes in financial decisions.
Retail applications involve product categorization, customer behavior analysis, and inventory management. The labeled data helps create personalized shopping experiences and efficient operations.
Agricultural applications include crop disease detection, yield prediction, and soil analysis. Labeled data helps farmers make data-driven decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
Successful data labeling requires clear rules, consistent methods, and proven strategies that ensure quality and efficiency throughout the process. Following established best practices helps organizations avoid common pitfalls and create training data that delivers reliable results.
Maintaining labeling consistency requires detailed guidelines, regular training, and standardized quality metrics. This ensures all labelers follow the same criteria when making decisions. Here are a few measures that you can incorporate to ensure consistency standards:
Error resolution is critical to maintaining high-quality labeled data. Ambiguous cases and disagreements among labelers can impact the data's consistency and reliability. Establishing clear processes for handling such issues ensures that labeling operations remain accurate and efficient.
Regular discussions and well-defined procedures help teams resolve conflicts, improve labeling standards, and ensure that the final output meets the desired quality criteria.
Here are steps to effectively resolve errors in data labeling:
Let's look at common hurdles teams face when labeling data and practical ways to overcome them, so you can avoid the same issues in your work.
Managing large-scale labeling projects is challenging as teams must balance speed, accuracy, and cost while dealing with massive datasets. This can lead to bottlenecks in workflow, uneven task distribution, and delays in meeting project timelines. Overworked labelers may also experience burnout, further affecting efficiency and output quality.
Solution:
To overcome these challenges, optimize workflows by breaking tasks into manageable steps and assigning specialized teams for different labeling categories. Use automation tools, like AI-assisted labeling, to reduce manual work and speed up the process. Implement scalable processes, such as cloud-based platforms, to handle growing data volumes efficiently.
Ensuring consistent labeling quality across a large team or complex dataset can be difficult. Differences in interpretation, lack of clear guidelines, and human errors can lead to variability, reducing the model's reliability.
Solution:
Establish a robust quality control system by providing clear labeling guidelines and conducting regular audits of labeled data. Create feedback loops to help labelers improve and use consensus reviews for complex cases. Quality metrics like Inter-Annotator Agreement (IAA) can be used to monitor and enforce consistency.
The true cost of data labeling often exceeds initial estimates, with expenses arising from workforce management, training, quality control, and tool licensing. Inefficient processes can lead to escalating costs, affecting project budgets.
Solution:
Understand and plan for all costs upfront, including indirect expenses like rework and tool upgrades. Use a mix of in-house resources and external vendors for flexibility. Evaluate automation tools for cost-effective scaling and focus on minimizing errors to avoid additional expenditures on corrections.
Quantifying the return on investment in data labeling can be difficult, as its impact is often indirect. Without clear metrics, it can be hard to justify the costs involved.
Solution:
Measure ROI by analyzing how improved data quality enhances model performance, leading to better predictions and business outcomes. Evaluate operational efficiency gains, such as faster product development, and the competitive edge achieved through higher-quality models. Maintain detailed records of labeling costs and their correlation with model performance to make data-driven investment decisions.
Data labeling remains a critical foundation for AI development. Success requires combining human expertise with efficient tools and processes while maintaining an unwavering commitment to quality.
The future of AI depends heavily on our ability to create high-quality labeled datasets. Organizations that master this fundamental aspect will be able to develop effective AI solutions.
LexiConn, the best content writing agency in Mumbai, has a skilled team to meet your data labeling needs, which helps businesses organize and mark their information correctly. Whether you have a small project or need help with large amounts of data, our experts deliver careful, accurate work on time.
Eager to get started? Drop us a line at [email protected] or visit our website to learn more. Avail our 30 min free consultation and free pilot to scale up your labeling projects!



I have read and accept the Privacy Policy
Read More