
Do you know what the future of eLearning courses looks like? According to GlobalNewswire, the eLearning market is expected to reach $457.8 billion by 2026. It’s no longer just about creating educational training materials—it’s about designing immersive, engaging experiences that lead to real-world results.
As the demand for eLearning courses grows, the focus is shifting from traditional methods to lively content that truly connects with learners.
In this blog, we’ll examine how content development for eLearning courses is changing and what it takes to create inspiring training courses.
Ready to improve your training programs? Here are a few steps to get you started!
Before diving into the content development process, you must clearly understand what you want your learners to achieve. To define learning goals effectively, start by asking yourself:
The purpose of your course should guide the structure and content. Is it to teach new skills, help learners pass an exam, or perhaps offer knowledge about a specific topic? This will provide the clarity needed to set precise goals.
When it comes to defining your eLearning course goals, it’s crucial to strike a balance between broad and focused objectives. If your goal is too broad, learners may struggle to see clear takeaways from the course.
On the other hand, overly focused goals can limit the scope of learning, leaving your course too narrow to engage a variety of learners.

In general, it's a good idea to start with a broad goal and then narrow it down into more specific, focused objectives. This allows you to create a course that balances both comprehensive learning and practical, measurable skills.
For example, if you start with a broader goal like “To improve communication skills in a professional setting,” you can break it down into focused, measurable objectives like:
Knowing who your learners are is a crucial part of course design.
The answers to these questions will influence how you structure your course, the language you use, and the type of content that will be most effective.
At Lexiconn, we recommend gathering insights into your audience’s preferences, challenges, and learning styles. This will help you build a course that is not only informative but also resonates with them.
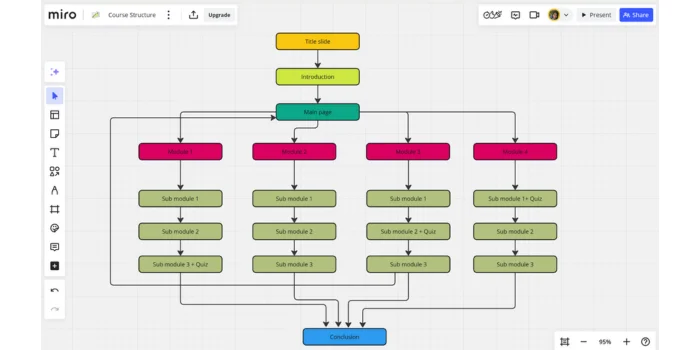
Once you’ve set your learning goals and understand your audience, the next step is to develop the structure of your course. This is where the outline of your developed content comes to life. A well-organized structure can make the learning experience smoother and more enjoyable. You can use tools like Miro to structure your course.
Here’s a general breakdown of what the structure could look like:
The introduction is your chance to grab learners' attention and set the stage for what’s to come. It’s essential to be clear and engaging from the start. In this section, you should:
|
Tip: Start with a few relevant quotes or insights that capture the essence of the topic. For example, use quotes that highlight the subject's importance or impact in real-life scenarios. This can create an immediate connection and encourage learners to see the value in what’s to come. |
This is the heart of your course. Breaking the content into training modules or lessons makes it easier for learners to digest and stay engaged. A typical training module structure could include:
Including assessments at key points throughout the course helps to:
The conclusion is your final opportunity to ensure learners walk away with key takeaways and a sense of accomplishment. Here, you should:
With the course structure in place, it’s time to craft a detailed script, which will serve as the foundation of your eLearning content. The script guides both on-screen text and any narration, shaping how information flows and how learners interact with the material.
A well-written script transforms the subject matter into engaging, accessible content, making it easy for learners to understand and retain key concepts.
There are two types of scripts often used in eLearning: on-screen text and narration script. Let’s go over the best practices for each.
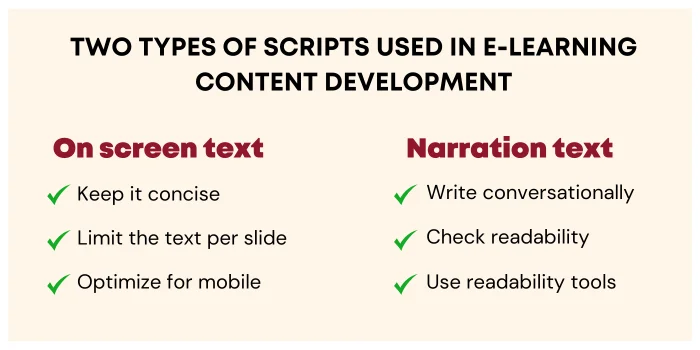
The on-screen text is all the text that appears directly on slides, so it’s essential to keep it focused and easy to read. To make on-screen text effective, consider these points:
For example, if you’re developing a content slide on “Customer Service Basics,” a single bullet point like “Listen actively to understand customer needs” is clearer than a long, descriptive paragraph. Supporting graphics or icons can make the idea even easier to grasp.
If your eLearning course includes voiceover, the narration script should sound conversational and easy to follow. This isn’t just text to read; it’s spoken content developed to engage listeners. A successful narration script will feel like a friendly guide leading the learner through each section. Here’s how to create one:
For example, if your script says, “We will now proceed to discuss the importance of communication in customer interactions,” a more listener-friendly version might be, “Let’s talk about why communication is key in working with customers.”
The on-screen text gives quick visual cues and supports the core ideas, while narration adds depth and a personal touch. Combining the two allows you to provide a richer, more interactive learning experience that can hold learners' attention and boost comprehension.
Learners are more likely to retain information if they actively engage with the content. This is where interactivity comes in. Interactive elements, like quizzes, drag-and-drop exercises, and role-playing scenarios, can significantly boost engagement.

Quizzes and tests are crucial for evaluating learners’ progress and reinforcing what they’ve learned. But not all quizzes are created equal. To make assessments more effective:
At Lexiconn, we often help design quizzes that align perfectly with the eLearning course material, ensuring they not only check knowledge but also support learning.
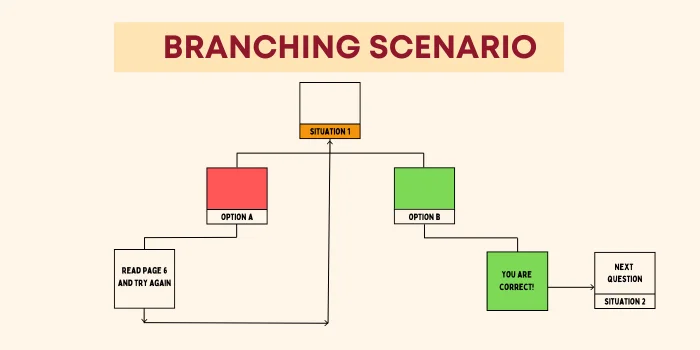
Branching allows learners to make decisions and see the consequences of their actions. For example, a sales training eLearning course might have a scenario where a learner has to choose the right approach to handle a customer complaint. Depending on their answer, they’re led down different paths that reflect the outcomes of their choices.
By integrating branching into your quizzes and assessments, you offer learners a more personalized, real-world experience.
To create branching in quizzes or assessments, you’ll need an authoring tool or platform that supports interactive or scenario-based learning, such as Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, or H5P. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building a branching scenario:
One of the most effective ways to teach soft skills or customer interaction techniques is through role-play scenarios. Creating realistic dialogue simulations lets learners practice in a risk-free environment. It’s an ideal way to develop communication skills, whether in sales, customer service, or management training.
These interactive simulations engage learners and provide immediate feedback, allowing them to learn from their mistakes and successes.
Creating an eLearning storyboard is crucial in developing effective and engaging content for an online learning course. It is a blueprint that bridges the gap between the developed content (script) and the design elements (graphics, visuals, audio). If you're new to storyboarding, don't worry!
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you understand the process in detail, with examples and suggestions to make it easier.
Before you begin developing a content storyboard, you’ll need some foundational materials. Think of this as gathering your ingredients before starting to cook. The more prepared you are, the smoother the process will be.
For example, if you're teaching an eLearning course on customer service, the script will outline key phrases and dialogue that should appear on the screen or be narrated by a voice actor.
For example, if you’re teaching data analysis, you might need to include a chart showing different data trends.
For example, it could show a slide with the text on the left and an image on the right, with the title at the top.
Once you have these materials ready, you can begin creating the storyboard with a clearer understanding of how everything will come together.
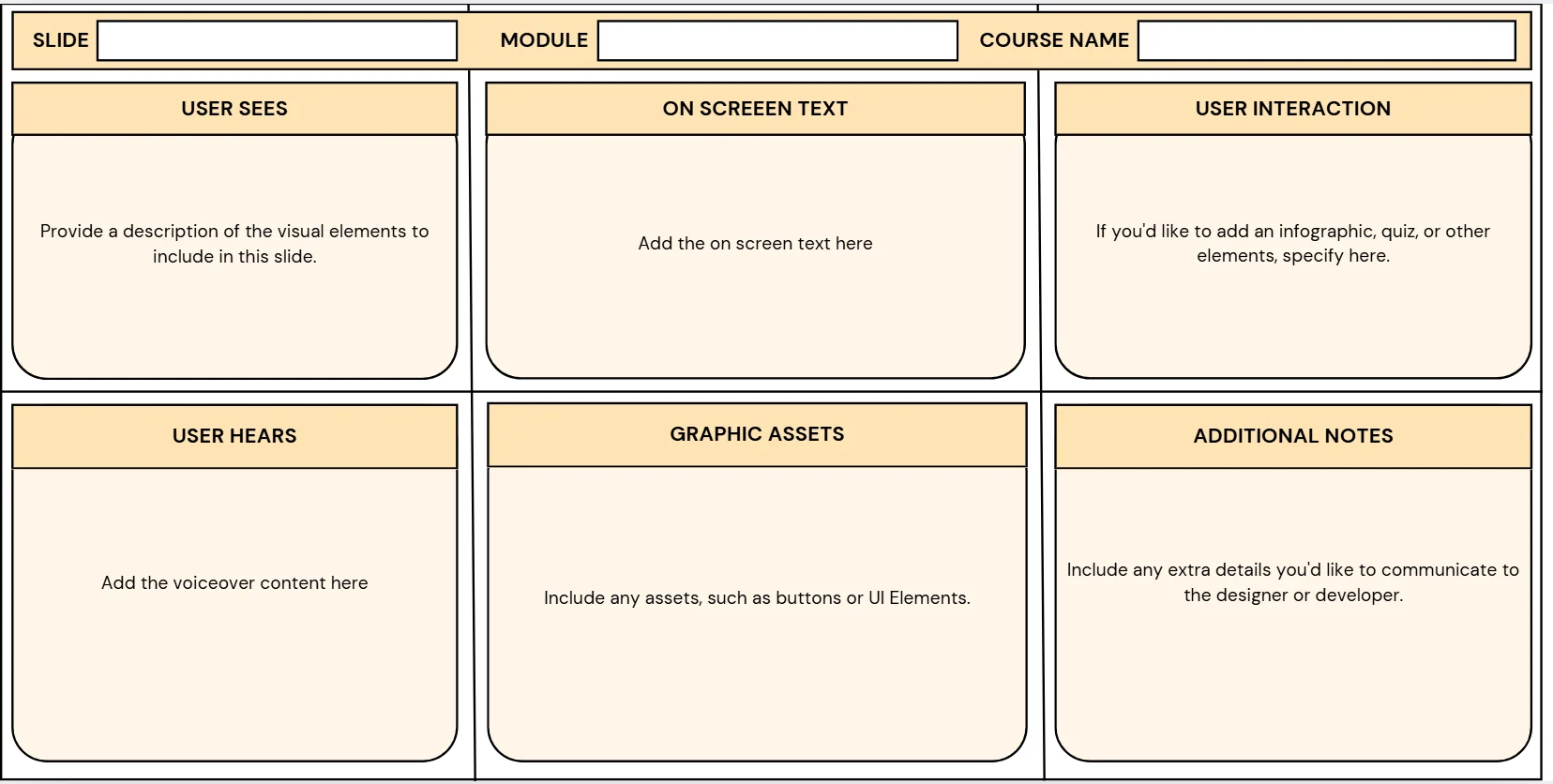
A storyboard template helps organize your thoughts and ensures you don't miss any important details. It’s a tool that simplifies the process and allows you to quickly capture the necessary information for each slide. You can find free templates online, such as those in Word, PPT, or PDF formats, or create your own.
Now that you have all the necessary pieces start filling out your storyboard. For each slide in your course, you’ll create a separate storyboard page. For simple slides (e.g., title slides), include just the text and any fixed design elements.
For more complex slides, like scenario-based learning, you might need to include multiple elements: the dialogue for characters, the actions they’ll take, and what will appear visually on-screen.
Let’s say you're building a scenario-based slide where learners must choose how to respond to a customer complaint. The storyboard for this slide might include:
The right tools can make a huge difference in how your content develops. If you're looking for tools to help create your eLearning course, Lexiconn can assist with writing all the textual content while ensuring it's optimized for both engagement and SEO.
But when it comes to tools for building the eLearning course itself, you’ll want to look at authoring software that suits your needs. These tools allow you to put together a professional-looking eLearning course easily. Here are some of the most widely used eLearning authoring tools:
It’s important to make your eLearning courses accessible to as many learners as possible. That means ensuring the developed content is mobile-friendly and accessible to people with disabilities.
This will help meet legal requirements and ensure a better experience for all learners.
Once you’ve developed and tested your eLearning course, it’s time to publish. Depending on your distribution goals, you’ll need to choose the right format.
With Lexiconn's experience in content development, we can help you optimize your eLearning course materials for whatever learning platform you choose, ensuring they reach your intended audience effectively.
Developing content for an eLearning course can seem overwhelming at first, but with a clear plan, the right tools, and effective content, you can develop an eLearning course that engages learners and delivers measurable results.
At Lexiconn, we’re here to help you through the content development process. We assist in writing engaging learning materials, designing assessments, or ensuring your course is accessible and mobile-friendly.
Experience our e-learning content with a free pilot to see the results firsthand. You can also schedule a free 30-minute consultation to explore the different types of e-learning modules we can design for you. Try it out and discover how we can develop your training content to be engaging and impactful!



I have read and accept the Privacy Policy
Read More