
Search engines and SEO content writing go hand in hand, and your URL structure plays a bigger role in this partnership. When search engines crawl your site, your URLs act as signposts, helping them figure out what your pages are about. At the same time, a clean, keyword-rich URL can make a huge difference for SEO, improving rankings and making your links more appealing to users. In this blog, we’ll explore how the right URL structure for SEO can work wonders for search engines and your site’s overall performance.
A URL is the address used to locate a resource on the internet. It has several key components serving a specific purpose:

The protocol is like a set of rules that helps your browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, etc.) talk to the website you're visiting. It tells your browser how to request information from the site and how to receive it back so you can see the page properly.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol): This is the standard protocol for transferring data over the internet. While it’s fast and commonly used, it doesn’t offer any encryption, meaning that the data sent between the browser and server is vulnerable to being intercepted by malicious third parties.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure): HTTPS is the more secure version of HTTP. It uses encryption (SSL/TLS) to protect data during transfer, making it more secure and private. With HTTPS, data sent between your browser and the server is encrypted, ensuring that even if someone tries to intercept it, they won’t be able to read it.
|
Tip: Google considers HTTPS a ranking factor, meaning secure websites have a higher chance of ranking in search results. |
The subdomain appears before the main domain name and is used to organize content into separate sections. Subdomains act as independent parts of a website.
Common subdomain: www (e.g., https://www.example.com)
Custom subdomains:
Blog: https://blog.example.com
Support: https://support.example.com
|
Tip: While subdomains can be useful, creating too many can confuse users and dilute your site's focus. Use them only when necessary. |
The domain name is the main part of a website address, and it's what makes your website unique on the internet. It's like the name of your house or business that people use to find you.
For example, in https://www.lexiconn.in, "lexiconn" is the domain name. It tells your browser where to go when you type in the address.
A domain name usually represents the name of your brand or business, so it’s easy for people to remember.
|
Tip: A good domain name helps people find your website easily, and it can even help improve your ranking on search engines. So keep it simple and relevant. |
The TLD is the extension that comes after the domain name, typically following the dot. It helps identify the type or purpose of a website. The TLD can help establish trust and credibility for your website.
Common TLDs:
.com – Commercial websites (e.g., https://www.example.com)
.org – Organizations (e.g., https://www.nonprofit.org)
.edu – Educational institutions (e.g., https://www.university.edu)
Country-specific TLDs:
.uk for the United Kingdom (e.g., https://www.example.co.uk)
.in for India (e.g., https://www.example.in)
|
Tip: Using the right TLD can make your site more relevant to specific audiences or regions, and the right URL structure can impact SEO, as search engines might prioritize country-specific TLDs for local searches. |
The path comes after the domain name, and it is the part of the URL showing the exact location of a specific page, post, or file within a website. It helps organize the content of the site into different sections or categories, making it easier for visitors to navigate.
Example:
Blog page: https://www.example.com/blog
Specific article: https://www.example.com/blog/seo-tips
The path can also include folders or subfolders that group similar content together. In the second example, "/blog/seo-tips" shows that the article on SEO tips is located within the "blog" section of the site.
|
Tip: A well-organized path helps both users and search engines find the content they’re looking for quickly. It also improves your SEO, as search engines may give higher rankings to URLs with clear, descriptive paths that match the content. |
The structure of your URLs plays a vital role in improving both search engine rankings and user experience. Here’s why it matters:
Search engines like Google depend on URLs to understand and organize website content. A clear, logical URL structure enables search engine bots to crawl and index your pages effectively.

Well-organized URLs signal relevance and hierarchy, helping search engines categorize your content correctly.
URLs that are simple and descriptive provide users with immediate context about the page content, encouraging them to click.

When users can predict where a link will take them, trust and engagement increase.
Adding relevant keywords in your URLs enables search engines to understand the topic on the page and can boost rankings for those keywords.

Keywords in the URL act as an additional relevancy signal, supporting your overall SEO strategy.
Clean URLs are more shareable and clickable, especially when users encounter them on social media, emails, or other platforms.

Short, clear URLs are easier to copy, paste, and share, leading to higher click-through rates.
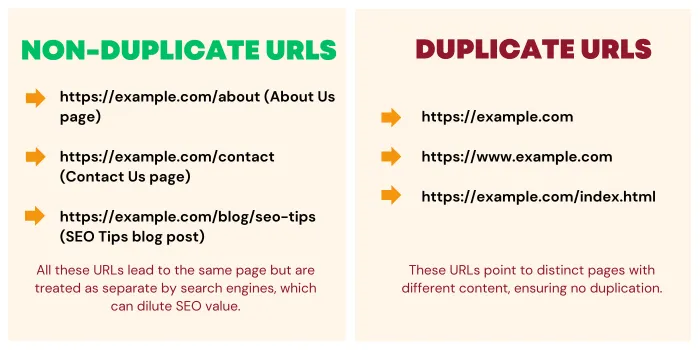
A consistent URL structure helps avoid duplicate content problems that can arise when multiple URLs point to the same page. Canonical tags and redirects can further assist in consolidating duplicate URLs.
A canonical tag is an HTML element used to tell search engines which version of a page is the "preferred" or "main" version when there are multiple URLs with similar or identical content.
A well-structured URL enhances user experience and helps search engines understand your content better. Let’s dive into some of the best practices to follow for optimizing your URL structure for SEO success.
Short URLs are like a friendly handshake—they’re easy to read, remember, and share with others. Plus, search engines love them, too, often ranking them higher in results.
To create a great URL, think about the main focus of your page and use clear, descriptive keywords that make sense at a glance. Avoid stuffing in extra words or unnecessary characters—keep it clean and simple, so both users and search engines know exactly what to expect.
Example:
Instead of: www.example.com/1234abc
Use: www.example.com/seo-tips
Adding relevant keywords in your URL enables search engines to understand your page's topic, improving its chances of ranking for related searches. Choose the most important keywords that reflect your content and optimize the URL structure for SEO for the best SEO impact.
Example:
Correct: www.example.com/seo-tips
Too much: www.example.com/best-seo-tips-for-beginners-and-experts
Using hyphens in URLs helps search engines like Google separate words, making it easier for them to understand the content. Underscores, however, aren't treated the same way. Optimize the URL structure for SEO with hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words for better ranking.
Example:
Preferred: www.example.com/seo-tips
Not preferred: www.example.com/seo_tips
A clear URL structure reflects an organized website, ensuring easy navigation for search engines and users. It helps establish a logical hierarchy, with broader sections leading to more specific content. To create this, start with your homepage and break your content into categories and subcategories that make sense.
Example:
Homepage: www.example.com/
Blog Section: www.example.com/blog/
Specific Post: www.example.com/blog/seo-tips
Static URLs are cleaner, easier to read, and favored by search engines. Dynamic URLs with parameters (like ?id=123) can cause confusion and duplicate content problems. If dynamic parameters are necessary, manage them with canonical tags or redirects. Ideally, stick to clean, descriptive URLs for better SEO.
Example:
Better: www.example.com/product-name
Less ideal: www.example.com/?id=123
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data exchanged between the server and the user's browser, enhancing security. Additionally, Google considers HTTPS a ranking factor to increase the likelihood of secure sites ranking higher.
To implement it, make sure your website has an SSL certificate and switch from HTTP to HTTPS, which helps build trust and improves your SEO performance.
Example:
Secure: https://www.example.com
Not secure: http://www.example.com
Using capital letters in URLs can lead to duplicate content issues because search engines treat uppercase and lowercase letters as different URLs. This can create confusion and affect how your pages are indexed.
To avoid such problems and maintain consistency, it's best to use only lowercase letters in your URLs. This simple practice helps prevent indexing issues and ensures better SEO performance.
Example:
Correct: www.example.com/blog
Incorrect: www.example.com/Blog
Stop words like "and," "or," and "the" don't add much value to a URL and can make it longer and harder to read. Removing them helps create cleaner, more concise URLs that are easier to understand and more likely to perform well in search rankings.
To achieve this, focus on the core elements of your content, excluding filler words, and only include what's necessary for clarity and SEO purposes.
Example:
Preferred: www.example.com/best-seo-tips
Not preferred: www.example.com/the-best-SEO-tips
When you change or delete a page, setting up 301 redirects ensures that the SEO value of the old URL is preserved by permanently redirecting users and search engines to the new URL. Without 301 redirects, you risk losing traffic and harming your site's SEO performance.
To avoid this, make sure to implement 301 redirects from the old URL to the new one and check that all broken links are properly redirected, helping maintain visitor flow and search engine rankings.
Testing your URLs is crucial for spotting issues like broken links or crawling errors that can harm your website’s performance in search engines. Regularly checking ensures a smoother user experience and helps maintain strong SEO. To do this, use tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog to monitor and test your URLs for any errors. These tools help identify issues with crawling, indexing, or page load times, allowing you to address them promptly and keep your site running smoothly.
Using tools like Google Search Console can alert you to any 404 errors or crawling issues, allowing you to fix them before they affect your rankings.
So now you know how crucial a well-optimized URL structure is for boosting your SEO strategy, and you’ve got a winning combination for improving your website’s visibility and rankings.
Looking for SEO writing services? At Lexiconn, we specialize in SEO content writing that helps you optimize every aspect of your website, from URL structure to in-depth content creation. Our team ensures that your content is optimized for search engines and resonates with your audience. Take advantage of our free pilot for web content to discuss how to improve your SEO and online presence.
Reach out today and start seeing the difference in your digital strategy!



I have read and accept the Privacy Policy
Read More